Posts by Rachel Kohn
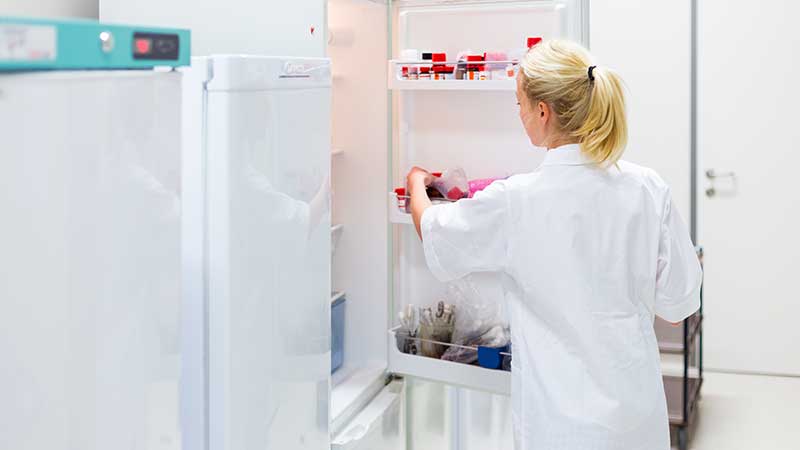
Laboratory Refrigerator Selection Criteria
Ultrasonic Passivation for Stainless Steel
Stainless steels such as AISI* Types 304, 310 and 316, are favored for strength and corrosion resistance. Applications include food, chemical and pharmaceutical processing, surgical implants, architecture and transportation. Over time starting from initial fabrication, free iron and other contaminants adhere to surfaces and must be removed. Ultrasonic passivation for stainless steel accomplishes this to…
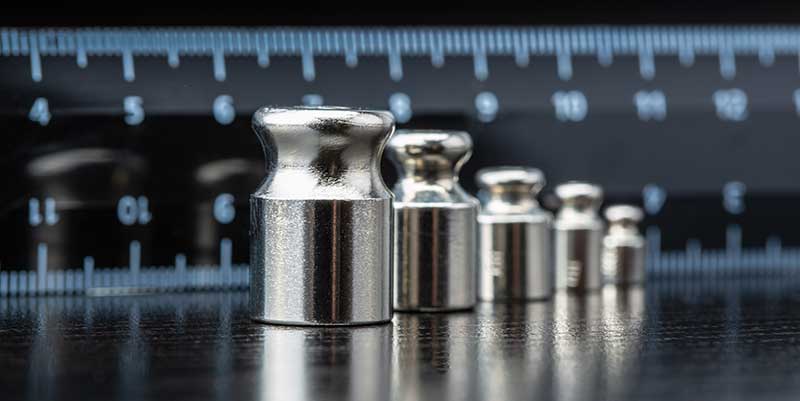
Selecting Scale Weights for Calibration Testing
Calibrating precision digital scales, analytical balances and moisture analyzers that rely on accurate weight measurement requires periodic tests using a scale weight closely matching the maximum capacity of the instrument being tested. Why Testing with Scale Weights is Important Daily we depend on weighing accuracy – such as visits to the deli counter in the…
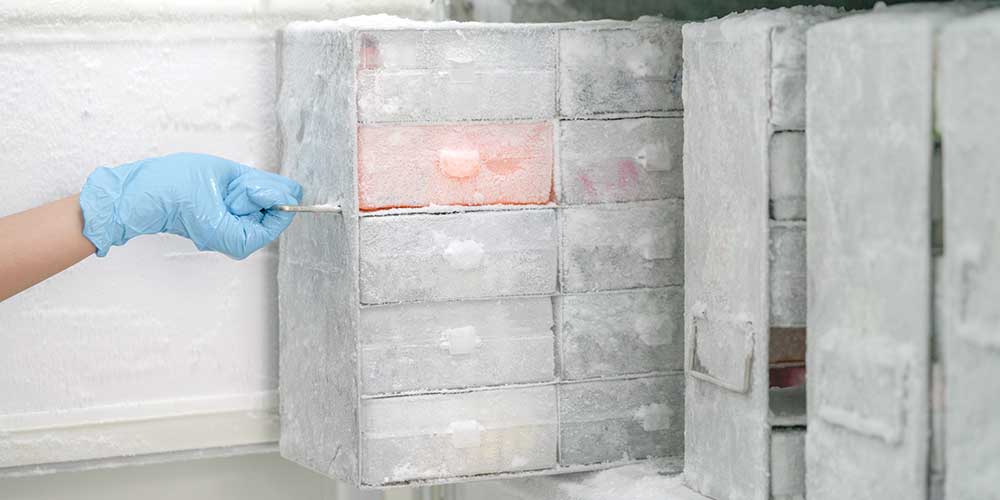
How to Specify a Super Cold Freezer
Flow Meter Calibration for HPLC Pumping Systems
First of all, our HPLC flow meters are shipped factory calibrated along with an accompanying calibration certificate for a flow rate of 1.0 ml/min plus additional flow rates requested by the customer. The calibration certificate certifies that the displayed flow rate is within ±1% of the actual flow rate at each calibration point.
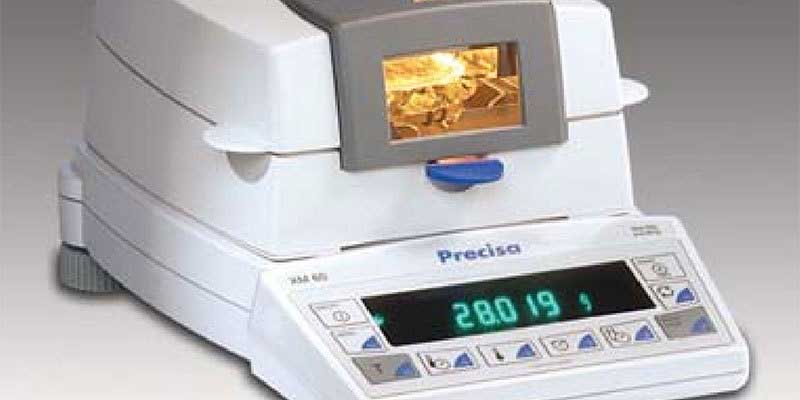
How to Determine Moisture Content
Ultrasonic Cleaning Tanks: What You Should Know
While a variety of ultrasonic cleaners are the market, one component they have in common is the ultrasonic cleaning tank where cleaning action takes place. Whether you select a basic model ultrasonic cleaner, an advanced benchtop or a floor-mounted industrial-scale model, long-term reliability depends on the industrial ultrasonic cleaning tank and how you use and…
Determining and Confirming Moisture Content in Food
As reported in Wikipedia, “Food moisture analysis involves the whole coverage of the food items in the world because foods are comprising a considerable amount of water rather than other ingredients.” Food Technology notes “Both moisture content and water activity… are important in formulating products for safety and stability.” This post describes how benchtop moisture…
Ultrasonic PCB Cleaners for New and Reconditioned Boards
Removing soldering flux and residues from new PCBs and dirt when reconditioning PCBs by using an ultrasonic PCB cleaner is faster and more gentle than soaking and scrubbing with sprays and solvents. Manual PCB cleaning is time consuming, can damage delicate PCB assemblies and can be environmentally unfriendly. An ultrasonic PCB cleaner provides your best…
Ultrasonic Cleaning Once-Fired Brass
A Tovatech Case Study A recent report by IBISWorld states that the U.S. Shooting Range Industry market is estimated at $4 billion and encompasses more than 11,000 businesses. Many shooting enthusiasts, whether pistol or rifle, save on the cost of purchasing new ammo by cleaning and reloading spent cartridges, called once-fired brass. Here we describe…